Know All About History of Evolution of Mutual Funds in India
What is Mutual Fund?
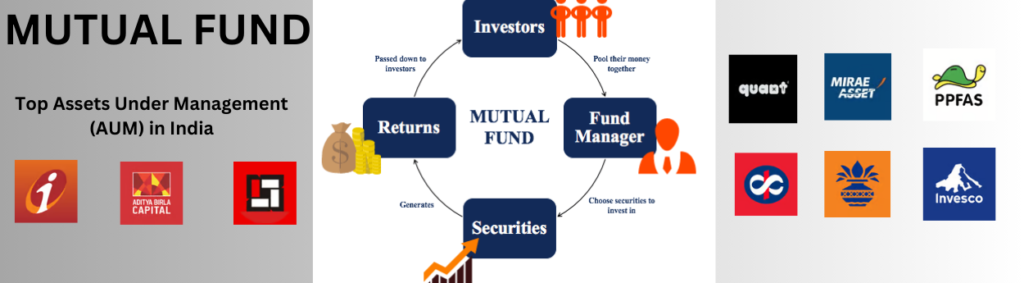
In a mutual fund, a group of investors pool their hard-earned money and give it to an investment manager, who invests on their behalf. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) is an independent organization that supervises the funds.
Know about the history and impact of mutual funds on India’s economic development. And the significance of credit-based financing and financial securities obtained through the capital market in shaping a country’s economic development. Furthermore, it will expand on previous research on mutual funds in India and their return predictability.
In our traditional investment approach, we favoured gold, real estate, and fixed deposits. However, the dynamic landscape of mutual funds has redirected our focus to the intricate world of financial markets. Guided by Asset Management Companies (AMCs), these funds not only pursue returns but also operate under the watchful eye of SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India), the vigilant guardian of the market.
Our traditional investing strategy prioritized fixed deposits, gold, and real estate. But the ever-changing mutual fund industry has forced us to shift our attention to the complex realm of financial markets. These funds, managed by Asset Management Companies (AMCs), seek returns while being closely monitored by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India), the market’s watchdog.
Significant Points in the Development
The Unit Trust of India (UTI), a joint venture between the Reserve Bank of India and the Government of India, was established in 1963, marking the beginning of the mutual fund business in India. This important historical evolution can be divided into four noteworthy stages.